Phishing attacks are on the rise and could be one of the most common types of internet attacks you have encountered. These scams have become even more dangerous as it targets people to hand over sensitive information like bank details, credit card, and login information.
What is Phishing?
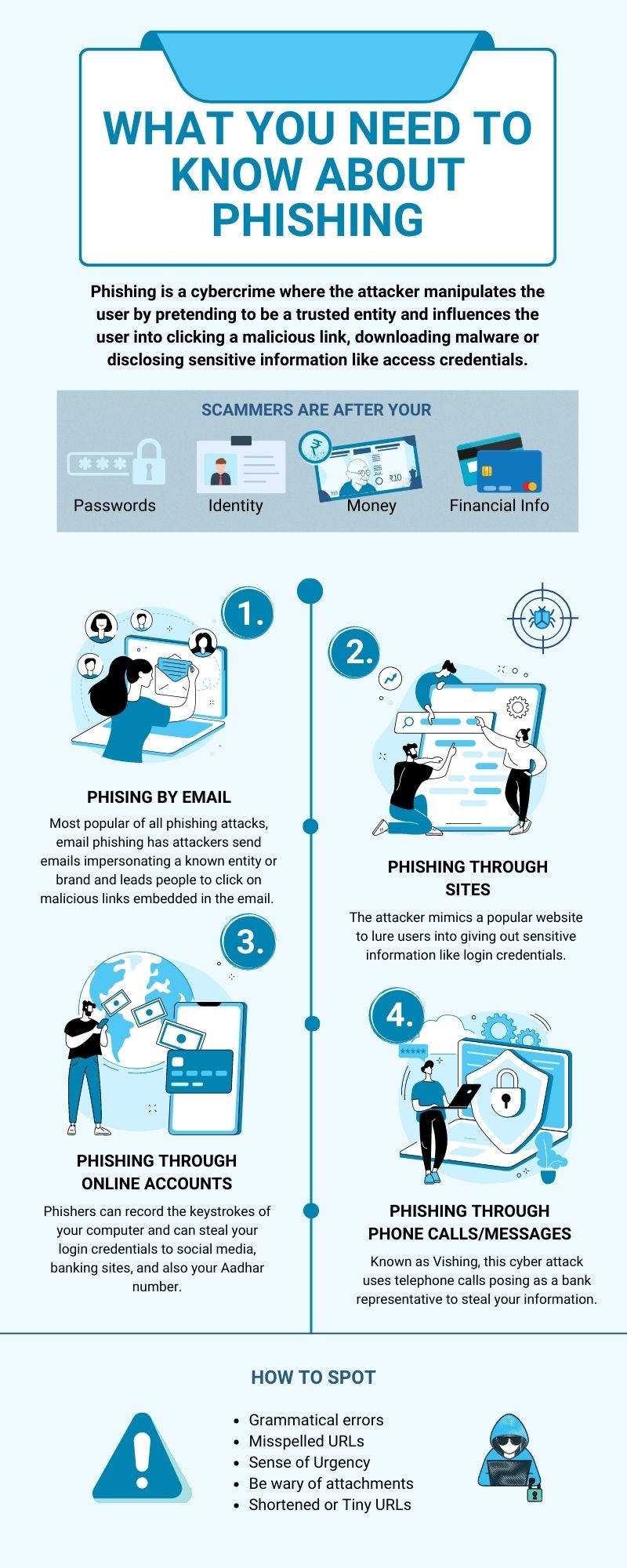
Phishing is a cybercrime where hackers use fraudulent practices to pose as a legitimate source and trick people into divulging sensitive data. In this type of cybersecurity attack, the attacker manipulates the user by pretending to be a trusted entity and influences the user into clicking a malicious link, downloading malware, or disclosing sensitive information like access credentials.
What are the types of Phishing?
There are many ways cybercriminals deliver malware to target users. Let us look at the top five types of phishing attacks.
- Email Phishing
Email phishing is the most common of all phishing attacks where malicious actors send emails impersonating a known entity or brand, capitalising on their social engineering tactics to lead people into clicking malicious links embedded in the email. These links usually lead to a downloaded PDF which installs malware on the system when opened and steals relevant credentials. - HTTPS Phishing
The Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure uses a two-way encryption protocol to communicate between a browser and a server. The hackers use this URL phishing technique to create a landing page that the user arrives at, thus downloading or clicking on malicious content. These links are often shortened links or hypertexts embedded into a text to hide the real URL. - Spear Phishing
Spear phishing is a type of email phishing but more sophisticated. Here the fraudsters gather all the information about a user beforehand, especially through social media or a company’s website. They target specific individuals using real names and job titles of persons within the same company to make the recipient think that the emails are genuine. These emails will have abnormal links to documents stored on shared drives like Google Suite or Office 365 which can redirect to a malicious website. - Whaling
Whaling or CEO fraud is similar to spear phishing where fraudsters use social media or company information to get the CEO, CFO, or a senior official’s whereabouts. They impersonate this official using a similar email id and ask for a money transfer, review a document, or declare you are facing a legal notice and that you should provide the necessary information by clicking a link. These links will ask you to enter your PAN ID, bank account numbers and other important details. - Vishing
Vishing is a type of security attack which uses telephone calls to steal your information. They could pose as a bank representative to encourage you to give out your credit card and bank account details.
How does Phishing work
If you are using the internet, you are a target of phishing scammers and there are many ways these fraudsters use to steal sensitive information from you, namely gathering relevant details from your social media like Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter or even the company one works at. With this information, the attacker could
- Infect your device with a malware
- Take control of your bank account
- Steal your credentials to get money
- Even blackmail you to send money or valuables, ransomware.
One should be wary of emails and other communication methods designed to lure you into providing confidential information.
How to Protect Against Phishing Attacks
There are many ways to identify and protect against these phishing attacks. Phishing attackers follow a similar pattern in emails and other modes of communication to look legitimate. Let us see five ways we can identify these attacks.
- Identifying Phishing Scams
One of the common techniques used in phishing emails is fake domains that are lookalikes to a trusted domain. These scams take a real company’s domain, eg: @company.com to @cmpony.com to mimic the legitimate domain. - Have a Filtering System
It is important that a filtering system is in place to screen and limit malicious websites. Happinetz Box uses a multi-level filtering system that screens and filters out phishing attacks and age-inappropriate content by tracking more than 110 million websites and app across the internet. The database is updated regularly to stay ahead of the filtering technology. - Do not click on Pop-Ups
Pop-ups are often linked to malware. They deceive you into where the close button is and thereby download malware into your computer when you click elsewhere. Install an ad-blocker that will automatically block most of the malicious pop-ups. The Happinetz System blocks a good number of malicious pop-ups. - Do not give out personal and financial information
Do not give out your card information or PAN card details to any site. Before you give out any such crucial information, verify that the website or app is 100% genuine. Check if it is a secured site with https or a closed padlock in the URL. Check each and every letter of the URL because some phishing attacks are so sophisticated in mimicking a branded site. They can record your keystrokes to steal any login or banking information. - Block Malicious Websites
Manually blocking every malicious website in the world is a near-impossible task. But the Happinetz System does it for you by filtering more than 4 million malicious websites and apps. It sends all the app and website requests to a central filtering system which determines whether the requests should be permitted or denied. By default, all adult and unsecured websites and apps are blocked by the Happinetz system.
Last, but not the least, it is crucial to understand that one should never respond to any spam. Keep your browser updated and change passwords regularly.
The better way to protect yourself from such phishing attacks is to set up a filtering system.
The Happinetz Box gives you safe internet especially for kids by having a multi-level filtering system, namely, Selective Access Control, MAC-based filtering, DNS filtering and Web Categorization. It blocks out malicious websites and apps and helps you prevent phishing attacks and data breaches.
FAQs
- How Does Happinetz Box Protect Against Phishing Attacks?
Happinetz Box protects against phishing attacks by filtering more than 4 million malicious websites and apps. This is done by sending all the apps and website requests to a central filtering system which determines whether the requests are legitimate and if they should be permitted or denied. This multi-level filtering system follows Selective Access Control, MAC-based filtering, DNS filtering and Web Categorization. By default, all adult and unsecured websites are blocked by the Happinetz System.
- What happens if you click a phishing link?
Here are a few likely scenarios that will occur when you click on a phishing link.
- The hacker receives basic data like the device statistics, your location, and any information that you may have voluntarily provided.
- Malware is downloaded and installed on your system. These could be spyware, ransomware, or any malicious file that can gain access to your system remotely or record your keystroke which is what you type on your computer. This malware can gain access to your login credentials and other confidential information.
- What helps protect from spear phishing?
Here are some great ways that you can protect yourself from spear phishing.
- Train your employees on security measures.
- Use multi-factor authentication
- Implement strict password policies
- Maintain regular software patching and updates
- Perform regular backup
- What is clone phishing?
Clone phishing is a type of cyber attack where the attacker clones and replicates a real or legitimate email message with the aim of spreading malware. There is a sense of urgency in these messages which often poses like they are from Amazon, PayPal, or your bank which will in turn coax you into logging into your account.
- What is URL phishing?
In URL phishing, the attacker mimics a familiar and popular website to lure users into giving out sensitive information like your login credentials. This is initiated by sending malicious emails to a possible victim which contain a URL to a fake website. When the victim clicks on this link, the attacker gets all sensitive information like usernames, passwords, and bank and social media credentials.
- What is executive phishing?
Executive phishing is also known as Whaling or CEO attack where the hacker impersonates senior officials or executives of a company and sends emails containing malicious websites to the company’s employees in order to steal their confidential information.
- What is a common indicator of a phishing attempt?
Here are some common indicators of phishing attempts.
- Spelling and Grammatical errors: Incorrect capitalization, and punctuation marks,
- Suspicious links or attachments: Check the legitimacy of the email before clicking on any message with suspicious links or attachments.
- A sense of urgency: If there is a sense of urgency making you want to act quickly, like a warning that your account will be suspended, or you need to change your password immediately, it is likely to be a phishing scam.
- Abnormal email addresses and domain names: Fraudsters usually mimic a legitimate company by changing only one or two letters of the right email or domain. Read the email carefully and hover over the hyperlinks to see where you are going to be redirected before clicking the hyperlinks.
- Emails coded entirely as hyperlinks: The hackers code the entire email into hyperlinks so that the entire email becomes clickable.




